Home > Chapter 1: What is Academic English?
1b: General Features of Academic English
Academic texts are characterised by a specific style with the following four features:
i) formality
ii) objectivity
iii) precision
iv) technicality
iv) Technicality
Subject-specific or technical vocabulary is essential to understanding and writing academic texts. To understand and retain the subject-specific vocabulary better, it is crucial to understand how these words are formed. For example, the prefix “photo-” means “light”, so the words “photosynthesis” and “photoconduction”, which can be found in science texts, are both related to “light”. Likewise, the suffix “-ism” means “a belief, theory or practice”. Words like “feudalism” and “Marxism”, which can be found in history texts, carry this meaning. The meanings of some subject-specific words may vary in different subjects or contexts. For example, the common word “mean” has a special meaning in mathematical contexts (i.e. average).
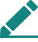 Activity 6
Activity 6
The words in the left column below are words with multiple meanings in different subject contexts. Match them to the appropriate subject(s) by putting a tick ( ) in the appropriate box(es). Consult a dictionary if needed. One of them has been done as an example.
| Words with multiple meanings | Subjects | ||||||
| Geography | Science | History | Maths | P.E. | Music | Economics | |
| e.g. current | |||||||
| legend | |||||||
| scale | |||||||
| class | |||||||
| note | |||||||
| slope | |||||||
| axis | |||||||